Cybersecurity Budget 2026: What CISOs Are Really Investing In Next Year
Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern; it’s a boardroom priority. As organizations adopt AI, embrace digital transformation, and move workloads to the cloud, securing systems has become increasingly complex. In 2026, CISOs are shifting from reactive spending to strategic, risk-based investments, focusing on protecting critical assets and reducing organizational risk.
According to a Gartner survey of 2025, 85% of CEOs say cybersecurity is critical for business growth, illustrating that security strategy now extends well beyond traditional IT functions and into core business planning.
The key question is: how are cybersecurity budgets evolving, and where are organizations prioritizing their resources? The Cybersecurity budget 2026 is no longer about simply spending more; it’s about investing in areas that deliver maximum protection, resilience, and measurable business value.
Are Cybersecurity Budgets Increasing in 2026?
Recent analyst projections indicate that cybersecurity budgets are rising globally, as organizations respond to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, stricter regulatory requirements, and growing demands for business continuity.
Gartner forecasts worldwide cybersecurity spending will reach $240 billion by 2026, up from $213 billion in 2025 (Gartner, 2025).
Cloud-native security, AI-powered threat detection, and managed services are primary drivers of increased investment (ComputerWeekly, 2025).
CISOs are not simply increasing budgets; they are ensuring that every dollar spent is strategically aligned with measurable outcomes, including risk reduction, regulatory compliance, operational resilience, and long-term cybersecurity efficiency.
The 2026 landscape is defined by smarter, more targeted investments that protect organizations against both current and emerging threats.
Key Drivers Behind 2026 Budget Growth
Several key factors are shaping how CISOs plan and allocate resources for the coming year.
1. AI-Driven Threats
Hackers are increasingly leveraging AI for automated phishing, deepfake social engineering, and adaptive malware. Organizations now require advanced AI-powered security tools for threat detection, incident response, and proactive threat hunting.
2. Cloud Expansion
The widespread adoption of multi-cloud environments, SaaS applications, and hybrid work models has significantly expanded the attack surface. CISOs are allocating larger portions of the budget toward cloud security solutions such as CNAPP, CWPP, and SASE platforms.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and emerging AI regulations demands stringent security controls. Organizations must invest in technologies and processes that ensure data protection, governance, and risk mitigation.
4. Talent Shortage
The global cybersecurity skills gap forces organizations to rely more on managed services, MDR providers, and outsourced SOC teams to maintain robust security operations.
5. Cyber Insurance Requirements
Insurers now mandate minimum security standards, driving additional budget allocation for compliance, risk mitigation, and incident preparedness.
These trends highlight that the Cybersecurity budget 2026 is not just about increasing spend, it’s about strategically investing in high-impact areas to maximize protection, resilience, and long-term business continuity.
2026 Cybersecurity Budget Forecast: What CISOs Expect
Analysts and surveys reveal how organizations are planning to allocate their Cybersecurity budget 2026 across key areas.
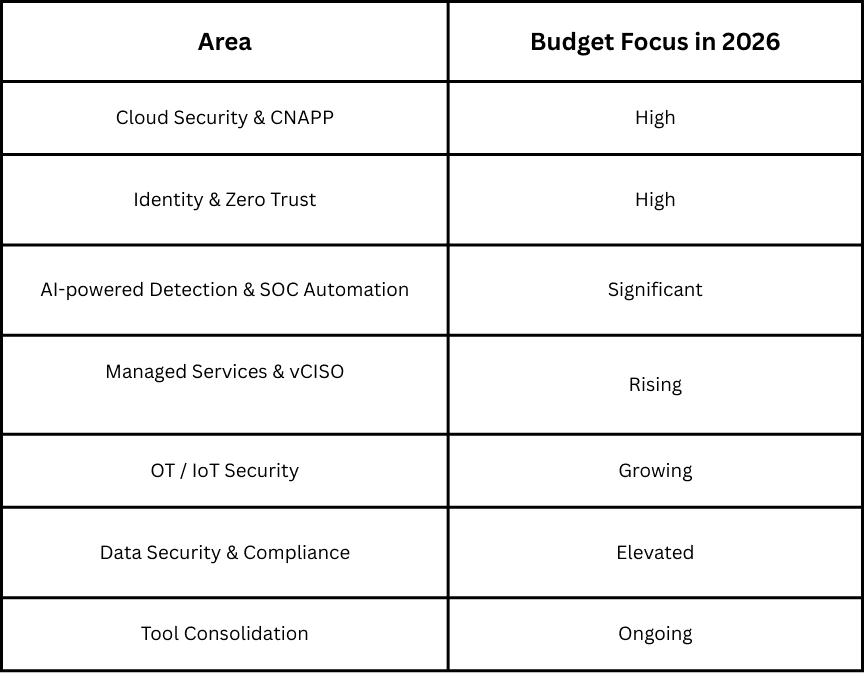
Security Software & AI-Powered Detection (30–35%): This includes XDR platforms, GenAI SOC copilots, automated incident response, and threat intelligence tools to help security teams detect and respond to threats faster.
Cloud Security & Posture Management (25–30%): Investments focus on CSPM, CWPP, CNAPP, and SASE solutions, reflecting the growing need to secure multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
Identity & Access Management (15–20%): Spending is directed toward PAM, MFA, Zero Trust implementation, and identity threat detection to protect critical access points.
Managed Services & MSSP Adoption (10–15%): Organizations rely on MDR, vCISO, and outsourced SOC teams to overcome talent shortages and ensure continuous protection.
Data Security & Compliance (10–12%): Budgets cover DSPM, data loss prevention, encryption, and regulatory governance to meet compliance requirements.
The Cybersecurity budget 2026 is clearly shifting toward strategic, high-impact areas, ensuring organizations are prepared for both current and emerging threats.
Source: Splashtop, 2026 Cybersecurity Trends
AI Is Driving Budget Increases in 2026
Artificial intelligence is both a threat and an opportunity:
Threats: AI-generated phishing and social engineering are 99% more convincing than traditional attacks. Deepfake attacks are rising. (Gartner, 2025)
Opportunities: Organizations are deploying AI for automated threat detection, SOC workflow optimization, and attack simulations.
Budget allocation for AI-driven security platforms and automation tools is expected to increase significantly in 2026.
Cloud Security & Zero Trust: The Dominant Focus
Cloud security continues to dominate cybersecurity budgets:
Cloud-Native Security Tools: CSPM, CWPP, CNAPP, CASB, and SASE solutions ensure comprehensive cloud protection.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Required in regulated industries, Zero Trust spending includes continuous authentication, micro-segmentation, and least-privilege access models. (Splunk, 2025)
Organizations are moving away from legacy firewalls and VPNs toward modern cloud-first security architectures.
OT/IoT Security: Expanding the Attack Surface
Operational Technology (OT) and IoT devices represent a growing risk:
- Industrial control systems, healthcare IoT, and smart city infrastructure require specialized security solutions.
- CISOs are allocating budgets to monitor, detect, and respond to attacks targeting OT/IoT devices.
- Spending on IoT and edge security is expected to grow alongside cloud and identity investments.
Cyber Insurance Influences Budget Decisions
Cyber insurance is now a key driver of security budgets:
- Insurers require minimum security measures before providing coverage.
- Organizations invest in incident response plans, identity management, and cloud security to meet policy requirements.
- Failing to meet these standards can increase premiums or deny coverage.
Managed Services and MSSP Adoption
Due to the talent shortage, CISOs are increasingly relying on external expertise:
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) and Managed Detection & Response (MDR) teams supplement internal security operations.
- Virtual CISOs (vCISOs) and AI Security Officers provide strategic guidance without expanding full-time staff.
- Outsourced services are projected to absorb a larger share of the cybersecurity budget in 2026. (ComputerWeekly, 2025)
Tool Consolidation: Smarter, Efficient Spending
CISOs are consolidating security tools to reduce complexity and costs:
Reducing overlapping tools from 40+ to 15–20.
Prioritizing platforms that integrate cloud, identity, detection, and response.
Optimizing budgets for automation, efficiency, and measurable risk reduction.
Rising Costs of Cyber Incidents
Cyber risk is real and expensive:
- Average cost of a data breach: $4.45 million in 2023, projected to exceed $5 million by 2025–26 (Gitnux, 2025).
- Ransomware and supply-chain attacks can cost tens of millions in downtime, recovery, fines, and reputational damage.
These costs justify increased strategic cybersecurity spending.
The Strategic Role of CISOs
CISOs are no longer just technical leaders; they are business risk strategists:
- Communicate cybersecurity risk to boards in financial terms.
- Advocate for budgets that reduce exposure and prevent costly breaches.
- Introduce Deputy CISOs, AI Security Officers, and vCISOs to manage complex security ecosystems.
- Ensure cybersecurity is a business enabler, not just a technical requirement.
What to Expect in 2026: Key Takeaways
The overarching theme: strategic, risk-based, and measurable security investments will dominate the cybersecurity budget 2026.
Cybersecurity Budget 2026 is Strategic, Not Optional
In 2026, cybersecurity spend isn’t just rising; it’s becoming more targeted and strategic. CISOs are prioritizing AI-driven security, cloud protection, identity management, and OT security while consolidating tools and meeting regulatory and insurance requirements. The real focus is on investing wisely to reduce risk and strengthen business resilience.
A smart, well-structured cybersecurity budget for 2026 is now essential for protecting trust, continuity, and competitiveness.
Execweb helps you connect to Fortune 500 companies. Contact us now







Comment